
Industrial furnaces and high-temperature equipment are constantly exposed to harsh environments—intense heat combined with aggressive chemical corrosion. Over time, these conditions can severely degrade furnace linings, leading to costly downtime, maintenance, and potential safety risks. For industries ranging from glass manufacturing to metallurgy, selecting refractory materials with exceptional durability and corrosion resistance is critical for operational efficiency and long-term profitability.
This is where corrosion-resistant silica mullite bricks demonstrate a distinct advantage. Engineered through high-temperature sintering to achieve optimal phase composition, these bricks provide an outstanding balance of thermal stability and chemical resistance, addressing the fundamental challenges of modern industrial kilns and furnaces.
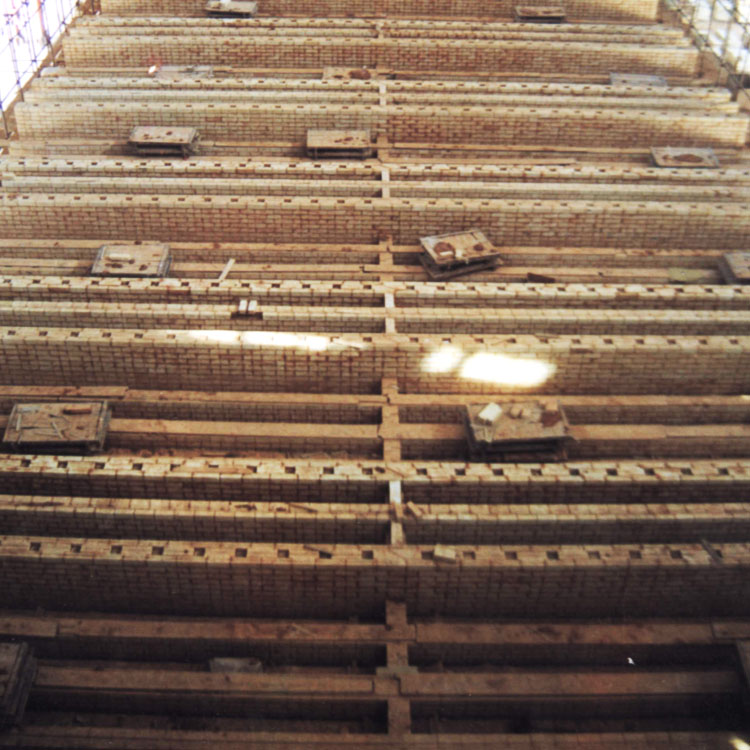

Silica mullite bricks are primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which after firing above 1600°C, form a dense, crystalline structure characterized by excellent high refractoriness and mechanical strength. Typically, these bricks withstand temperatures exceeding 1750°C while maintaining structural integrity. Their corrosion resistance derives from the chemical inertness of silica and the stability of mullite phases under oxidative and alkali environments.
| Parameter | Typical Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Refractoriness | ≥ 1750 | °C |
| Bulk Density | 2.55 - 2.65 | g/cm³ |
| Cold Crushing Strength | ≥ 120 | MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance (alkali & slag) | Excellent | — |
Among various industrial furnaces, glass melting furnaces represent one of the most demanding environments for refractory materials due to their prolonged exposure to high temperatures and corrosive glass melt. Corrosion-resistant silica mullite bricks have proven effective in lining glass furnaces, significantly reducing wear from molten glass and alkali vapors.
Case studies from leading glass manufacturers reveal that furnace linings reinforced with these bricks experience up to a 30% increase in service life compared to traditional fireclay bricks. This durability directly correlates with lower operational downtime and maintenance costs, which are crucial factors for maintaining production efficiency and controlling expenses.
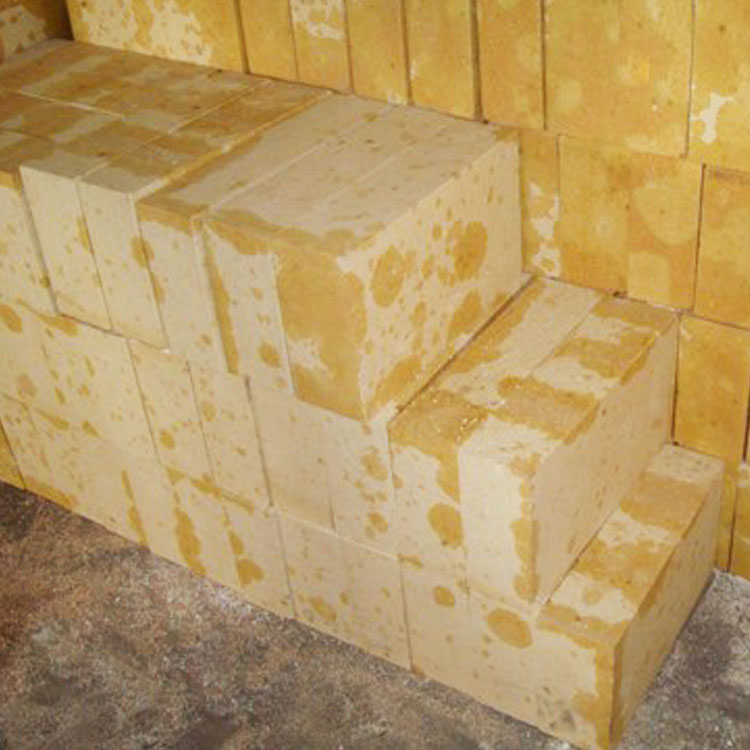

Besides glass production, these bricks are also widely used in industrial kilns for cement manufacturing, metallurgy, and chemical processing, where resistance to alkali and slag attack remains paramount. Their proven track record in these sectors further solidifies their role as a cornerstone material for industrial furnaces requiring both long-term reliability and cost-efficiency.
Employing corrosion-resistant silica mullite bricks is not solely a technical decision but a strategic business move. Companies that invest in these high-performance refractory linings gain multiple advantages:
These factors contribute directly to higher return on investment and reinforce the company’s position as a forward-thinking industry player.
Corrosion-resistant silica mullite bricks form a robust protective barrier within the demanding conditions of various industrial high-temperature furnaces. Their excellent balance of high refractoriness, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance makes them indispensable for companies aiming to safeguard equipment, optimize performance, and maximize profitability.
For procurement decision-makers worldwide, these bricks represent a reliable, cost-effective solution that enhances both operational reliability and competitive positioning in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.

