
When it comes to selecting refractory materials, global buyers often find themselves in a quandary. With numerous options available in the market, making the right choice can be a daunting task. Among these refractory materials, mullite bricks stand out as a reliable option due to their excellent high - temperature resistance and other remarkable properties. Understanding the different types of mullite bricks, their characteristics, and applications is crucial for buyers to make an informed decision.
Sintered mullite bricks are made from high - alumina bauxite or other high - purity raw materials. The production process involves crushing the raw materials, mixing them with appropriate additives, forming the mixture into brick shapes, and then sintering at high temperatures (usually around 1600 - 1800°C). This high - temperature sintering process enhances the density and strength of the bricks.
These bricks have excellent thermal shock resistance, with a thermal shock resistance of up to 30 - 50 times under normal conditions. They also have a relatively high refractoriness, typically above 1750°C, making them suitable for applications where sudden temperature changes are common.
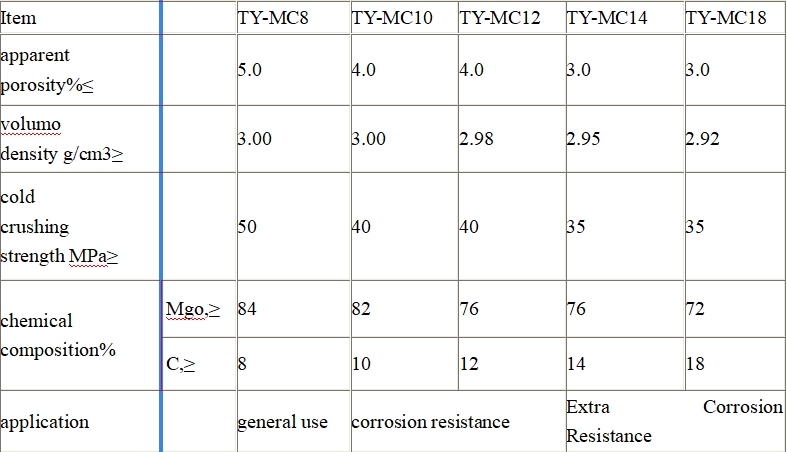
Fused mullite bricks are produced through an electric melting process. The raw materials, such as high - alumina bauxite and other additives, are melted in an electric arc furnace at extremely high temperatures (around 2000 - 2200°C). After melting, the molten material is cast into molds and cooled to form bricks.
Fused mullite bricks have a more uniform structure and higher purity compared to sintered mullite bricks. They have excellent corrosion resistance, with a corrosion rate of less than 5% in some harsh chemical environments. Their refractoriness can reach up to 1850°C, making them ideal for applications in highly corrosive and high - temperature environments.

| Aspect | Sintered Mullite Bricks | Fused Mullite Bricks |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | High - alumina bauxite, additives | High - alumina bauxite, additives |
| Production Process | Crushing, mixing, forming, sintering at 1600 - 1800°C | Melting in electric arc furnace at 2000 - 2200°C, casting |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent (30 - 50 times) | Good, but relatively lower than sintered bricks |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent (corrosion rate < 5%) |
| Refractoriness | Above 1750°C | Up to 1850°C |
In the metallurgical industry, sintered mullite bricks are often used in the lining of ladles and tundishes due to their good thermal shock resistance. Fused mullite bricks, on the other hand, are preferred in the lining of electric arc furnaces and steel - making converters because of their high refractoriness and excellent corrosion resistance.
In the glass industry, both types of mullite bricks can be used in the regenerators and melting tanks of glass furnaces. Sintered mullite bricks can handle the temperature fluctuations during the melting process, while fused mullite bricks can resist the corrosion of glass melt and flue gases.
In the ceramic industry, sintered mullite bricks are commonly used in the kilns for firing ceramics. Their thermal shock resistance ensures the long - term stability of the kiln lining.
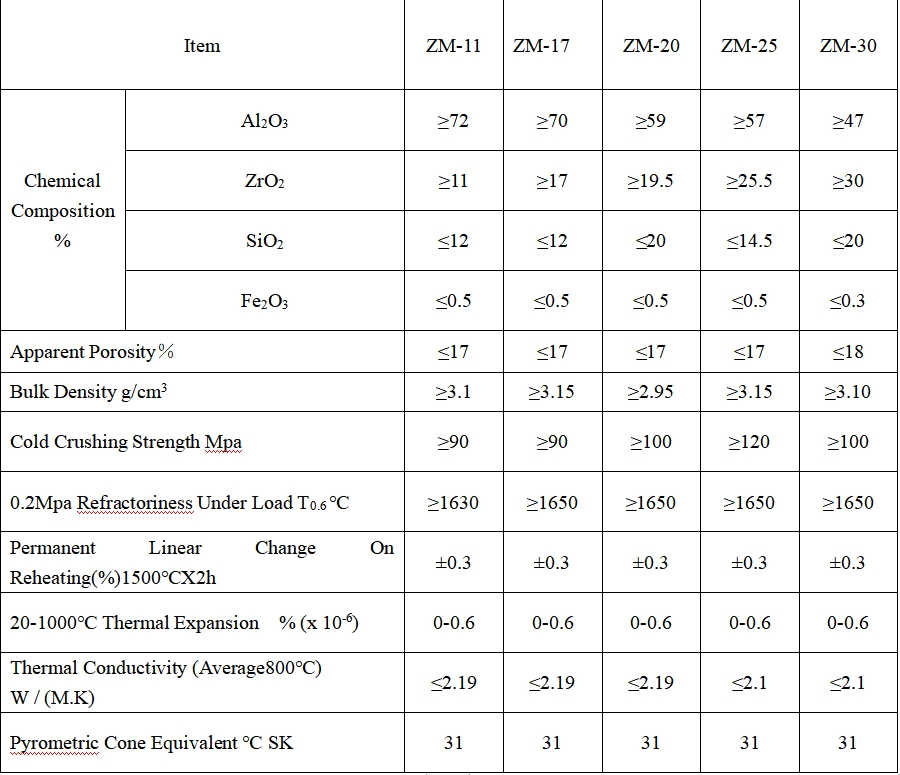
Sintered mullite bricks are known for their excellent thermal shock resistance, making them suitable for applications where temperature changes are frequent. Fused mullite bricks, with their high refractoriness and corrosion resistance, are ideal for harsh high - temperature and corrosive environments.
As a global buyer, it is essential to assess your specific requirements, such as temperature range, chemical environment, and thermal shock conditions, before choosing the right type of mullite bricks. By doing so, you can ensure the long - term performance and cost - effectiveness of your refractory lining.
Ready to make the right choice for your refractory needs? Contact us now to explore our high - quality mullite brick products and let our experts help you select the most suitable option for your application!

